- India
- Aug 30
Explainer / National Small Industry Day
The ministry of micro, small & medium enterprises observes National Small Industry Day on August 30 to promote small industries across the country.
India is home to more than 6.3 crore MSMEs, which have the ability and capability to access international markets and work as ancillaries to larger international firms.
Some important points on the MSME sector
• The Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) sector has emerged as a highly vibrant and dynamic sector of the Indian economy over the last five decades.
• MSMEs are an integral part of the value chain, offering diversified products on one hand and delivering intermediate goods for the large-scale industries on the other.
• It is one of the largest employment generators and backbone of Indian economy.
• Nearly 30 per cent of the GDP in Indian economy is contributed by the MSME sector.
• As per the National Sample Survey (NSS) 73rd round, conducted by National Sample Survey Office during the period 2015-16, there were 633.88 lakh unincorporated non-agriculture MSMEs in the country engaged in different economic activities.
• Micro sector with 630.52 lakh estimated enterprises accounts for more than 99 per cent of total estimated number of MSMEs. Small sector with 3.31 lakh and medium sector with 0.05 lakh estimated MSMEs accounted for 0.52 per cent and 0.01 per cent of total estimated MSMEs, respectively.
• Out of 633.88 estimated number of MSMEs, 324.88 lakh MSMEs (51.25 per cent) are in rural areas and 309 lakh MSMEs (48.75 per cent) are in urban areas.
• As per the survey, MSME sector has been creating 11.10 crore jobs (360.41 lakh in manufacturing, 0.07 lakh in non-captive electricity generation and transmission, 387.18 lakh in trade and 362.82 lakh in other services) in the rural and the urban areas across the country.
• Uttar Pradesh has the largest number of estimated MSMEs with a share of 14.20 per cent of MSMEs in the country. It is followed by West Bengal and Tamil Nadu, says the survey.
Some of the key reforms introduced by the MSME ministry:
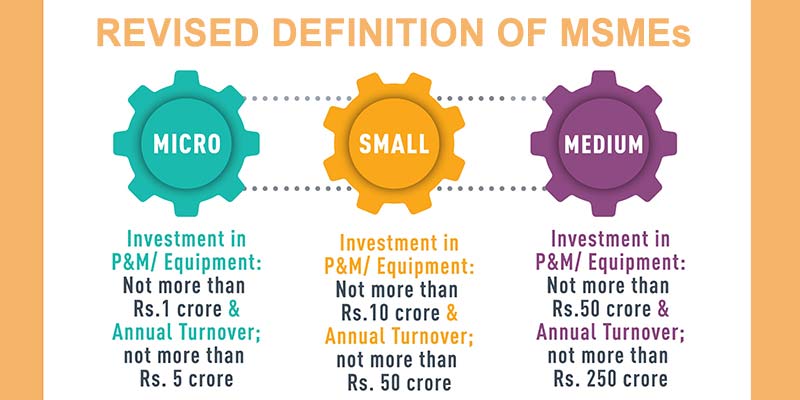
Revision of MSME definition: In line with the Centre’s top focus on energising MSMEs in the country, the government approved the upward revision of MSME definition on June 1, 2020 under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat Package. The government revised the MSME classification by inserting composite criteria of both investment and annual turnover.
The definition of micro manufacturing and services unit was increased to Rs 1 crore of investment and Rs 5 crore of turnover.
The limit of small unit was increased to Rs 10 crore of investment and Rs 50 crore of turnover.
Similarly, it increased the limit for medium manufacturing and service units. Now it will be Rs 50 crore of investment and Rs 250 crore of turnover.
This year, in July, Union Minister Nitin Gadkari announced inclusion of retail and wholesale trade under MSMEs as per which they will also now get the benefit of priority sector lending under RBI guidelines. The revised guidelines will benefit 2.5 crore retail and wholesale traders.
Udyam Registration: Udyam is an online and simplified procedure of filing of registration which enables MSMEs to obtain registration without any documentation and fees. It is a globally benchmarked process and a revolutionary step towards Ease of Doing Business. The ministry of MSME has also commenced API integration of Udyam Registration portal with Government e-Marketplace (GeM), so that MSEs can participate in government procurement easily.
CHAMPIONS Portal: CHAMPIONS (Creation and Harmonious Application of Modern Processes for Increasing the Output and National Strength) is an online platform to help and handhold the MSMEs. It is an ICT based technology system aimed at making the smaller units big by solving their grievances, encouraging, supporting, helping and handholding throughout the business lifecycle. The platform facilitates a single window solution for all needs of MSMEs.
National SC-ST Hub (NSSH): National SC-ST Hub has been launched to promote entrepreneurship culture in the SC-ST community and fulfill the 4 per cent procurement target mentioned in the Public Procurement Policy for MSEs Order, 2018.
To boost entrepreneurship among SC/ST population and for maximum on-ground penetration, several interventions have been undertaken to cater to the challenge of market linkages, finance facilitations, capacity building, etc.
Self-Reliant India (SRI) Fund: The scheme is expected to facilitate equity financing of Rs 50,000 crore in the MSME Sector. The infusion of equity will provide an opportunity to get MSMEs listed in stock exchanges. Further, it will also facilitate MSMEs to scale-up their business & growth and will help create more jobs in the MSME sector.
Procurement Policy: For providing marketing support to MSEs, all central ministries/government departments and CPSEs are required to procure 25 per cent of their annual requirements of goods and services from MSEs including 4 per cent from MSEs owned by SC/ST and 3 per cent from MSEs owned by women entrepreneurs under the Public Procurement Policy.
Establishment of Enterprise Development Centers (EDCs): With a view to provide information related to MSMEs at one place, Enterprise Development Centres (EDCs)have been conceptualised. The ministry of MSME has set up 102 EDCs across India. The aim of these centers is to build a network of entrepreneurial leaders by providing professional mentoring and handholding support services to existing as well as aspiring MSMEs with special focus on rural enterprises on a continuous basis.
Manorama Yearbook app is now available on Google Play Store and iOS App Store