- India
- Apr 09
Explainer / Atal Innovation Mission (AIM)
The Union Cabinet approved continuation of the Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) till March 2023.
Total budgeted expenditure of Rs 2,000 crore plus shall be incurred in the process of the establishment and supporting the beneficiaries.
The AIM shall work on its intended target of creating an innovation culture and entrepreneurial ecosystem in the country. This will be done by AIM via its various programmes.
The intended targets that will be achieved by AIM are:
i) Establishing 10,000 Atal Tinkering Labs (ATLs).
ii) Establishing 101 Atal Incubation Centers (AICs).
iii) Establishing 50 Atal Community Innovation Centers (ACICs).
iv) Supporting 200 startups via the Atal New India Challenges.
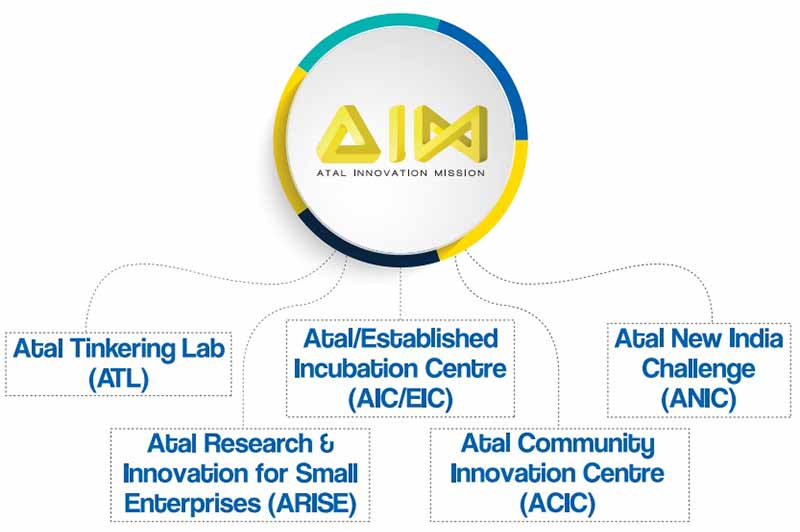
What is Atal Innovation Mission (AIM)?
• Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), set up in 2016, is government’s flagship initiative to foster innovation and entrepreneurship in schools, colleges and society at large and promote a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship in the country.
• AIM has taken a holistic approach to ensure creation of a problem-solving innovative mindset in schools and creating an ecosystem of entrepreneurship in universities, research institutions, private and MSME sector.
• All the initiatives of AIM are currently monitored and managed systematically using real-time MIS systems and dynamic dashboards.
Major initiatives undertaken by AIM are:
i) Establishment of Atal Tinkering Labs (ATL) in schools to create a problem-solving mindset in students between Classes 6-12. ATL is a flagship initiative of AIM to nurture an innovative mindset amongst high school students in India. ATLs encourage students to come up with out-of-the-box ideas. The programme is designed to equip students with skills such as design thinking, critical thinking, computational thinking, and digital fabrication. Under the scheme, grant-in-aid of up to Rs 20 lakh is provided to select schools to set up an Atal Tinkering Lab.
ii) Establishment of Atal Incubation Centres (AICs) in universities, institutions, and the private sector to foster world-class startups, as well as adding new dimensions of outcome-based scale-up and monitoring of existing incubator models. AICs aim to foster the entrepreneurial spirit while creating a supportive ecosystem for startups and entrepreneurs in India. AIM has been tasked with establishing and supporting world-class incubators.
iii) Launch of Atal New India Challenges (ANICs) to foster product and service innovations in the country with national socio-economic impact and aligning them to the sectoral needs of various ministries/industry and with the Sustainable Development Goals. ANIC is an initiative aimed towards selecting, supporting, and nurturing innovations based on advanced technologies in areas of national importance and social relevance, through a grant-based mechanism, while addressing bottlenecks due to which innovators are unable to access resources for piloting, testing, and market creation.
iv) Establishment of Atal Community Innovation Centres (ACICs) in the unserved/underserved regions of the country, including tier-2 and tier-3 cities and in the hinterland, to stimulate community-centric innovations and create local hubs of innovation and job creation. ACICs are a crucial step in building the budding startup ecosystem. They not only support up-and-coming entrepreneurs but also provide them with linkages to the developed start-up ecosystem, thus expediting their learning curve and stimulating faster growth. AIM offers financial support through grants up to Rs 2.5 crore to an ACIC subject to a partner proving equal or greater matching funding.
v) Launch of Applied Research and Innovation Challenges for Small Enterprises (ARISE-ANIC) to stimulate ‘Make in India’ research and innovations in the MSME ecosystem. The objective is also to provide a steady stream of innovative products and solutions for which the central ministries/departments can become the potential first-buyers. So far, AIM has identified 15 critical challenge statements with five ministries/departments.
vi) Establish a nationwide voluntary Mentors of Change network to support all the initiatives of AIM.
vii) Building strategic innovation partnerships with the public and private sectors and multinationals, and country-to-country partnerships to promote collaborations and cross-border innovation exchanges.
Major achievements of AIM:
• AIM-supported startups have raised Rs 2,000 crore plus from the government and private equity investors, besides creating several thousand jobs.
• The programmes of AIM cover 34 states and Union Territories with the goal of leveraging India’s demographic dividend by inspiring greater participation in the innovation ecosystem.
• The Mission has created bilateral relations with various international agencies for building synergistic collaboration on innovation and entrepreneurship such as the AIM – SIRIUS Student Innovation exchange programme with Russia, AIM – ICDK (Innovation Centre Denmark) Water Challenge with Denmark, and IACE (India Australian Circular Economy Hackathon) with Australia.
• AIM played a pivotal role in the success of InSpreneur, an Innovation Startup Summit hosted between India and Singapore.
• AIM partnered with the ministry of defence to set up the Defence Innovation Organisation which is fostering innovation as well as procurement in the defence sector.
Manorama Yearbook app is now available on Google Play Store and iOS App Store