- India
- Aug 08
Explainer / Governing Council of NITI Aayog
Prime Minister Narendra Modi made a strong case for modernising agriculture, animal husbandry and food-processing to help the country become self-sufficient and a global leader in the agriculture sector.
He was addressing the seventh meeting of the Governing Council (GC) of NITI Aayog.
The Prime Minister also asked the states to focus on promoting 3Ts — Trade, Tourism, Technology — with a view to reducing imports and increasing exports.
This was the first physical meeting of the Governing Council since the onset of the pandemic, with the 2021 meeting held via video conferencing.
The meeting was attended by 23 chief ministers, 3 lieutenant governors and 2 administrators and Union ministers. The meeting was moderated by Defence Minister Rajnath Singh.
The Governing Council discussed four key agenda items:
i) Crop diversification and achieving self-sufficiency in pulses, oilseeds and other agri-commodities.
ii) Implementation of the National Education Policy (NEP) in school education.
iii) Implementation of NEP in higher education.
iv) Urban governance.
Every chief minister and Lt Governor present at the meeting addressed the meeting, highlighting the priorities, achievements and challenges of their respective states and Union Territories with a special focus on the four key agenda items.
What is NITI Aayog?
• National Institution for Transforming India, better known as NITI Aayog, was formed via a resolution of the Union Cabinet on January 1, 2015.
• The government constituted NITI Aayog to replace the Planning Commission, which had been instituted in 1950.
• NITI Aayog acts as the quintessential platform of the government of India to bring the states to act together in national interest, and thereby fosters cooperative federalism.
• It is the premier policy think tank of the government of India, providing directional and policy inputs. Apart from designing long-term policies and programmes for the government of India, NITI Aayog also provides relevant strategic and technical advice to the Centre, states, and Union Territories.
• NITI Aayog is developing itself as a state-of-the-art resource centre with the necessary knowledge and skills that will enable it to act with speed, promote research and innovation, provide strategic policy vision for the government, and deal with contingent issues.
Team NITI Aayog
• The Prime Minister is the chairperson of NITI Aayog. The vice chairperson is appointed by the Prime Minister. Currently, there are three full-time members. Four Union ministers are nominated by the Prime Minister as Ex-officio members. Special Invitees are also nominated to NITI Aayog.
• Chief Executive Officer (CEO) is appointed by the Prime Minister for a fixed tenure, in the rank of secretary to the government of India.
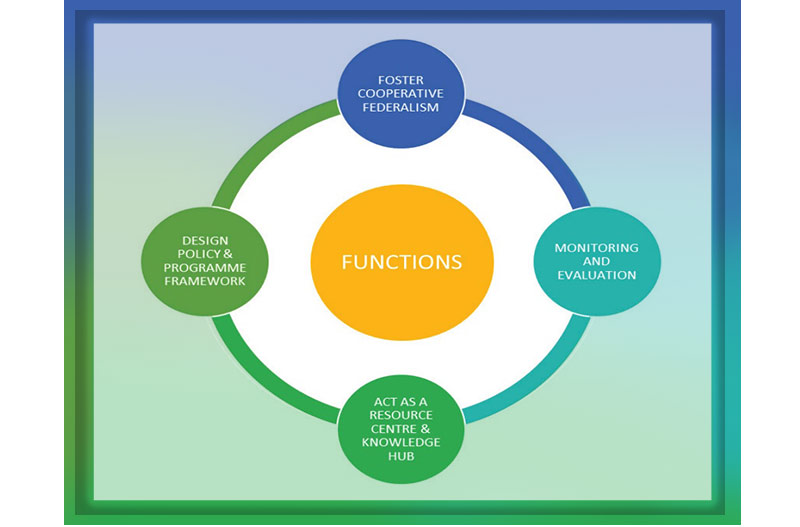
NITI Aayog’s entire gamut of activities can be divided into four main heads:
1) Policy and Programme Framework
2) Cooperative Federalism
3) Monitoring and Evaluation
4) Think Tank, and Knowledge and Innovation Hub.
• NITI Aayog plays an integrative role — with the active involvement of states, the civil society, and other think tanks — in development of a shared vision of national priorities and strategies in critical areas of human and economic development.
Objectives of NITI Aayog:
• To evolve a shared vision of national development priorities, sectors and strategies with the active involvement of states.
• To foster cooperative federalism through structured support initiatives and mechanisms with the states on a continuous basis, recognising that strong states make a strong nation.
• To develop mechanisms to formulate credible plans at the village level and aggregate these progressively at higher levels of the government.
• To ensure, on areas that are specifically referred to it, that the interests of national security are incorporated in economic strategy and policy.
• To pay special attention to the sections of our society that may be at risk of not benefiting adequately from economic progress.
• To design strategic and long-term policy and programme frameworks and initiatives, and monitor their progress and their efficacy. The lessons learnt through monitoring and feedback will be used for making innovative improvements, including necessary mid-course corrections.
• To provide advice and encourage partnerships between key stakeholders and national and international like-minded think tanks, as well as educational and policy research institutions.
• To create a knowledge, innovation and entrepreneurial support system through a collaborative community of national and international experts, practitioners and other partners.
• To offer a platform for the resolution of inter-sectoral and inter-departmental issues in order to accelerate the implementation of the development agenda.
• To maintain a state-of-the-art resource centre, be a repository of research on good governance and best practices in sustainable and equitable development as well as help their dissemination to stakeholders.
• To actively monitor and evaluate the implementation of programmes and initiatives, including the identification of the needed resources so as to strengthen the probability of success and scope of delivery.
• To focus on technology upgradation and capacity-building for implementation of programmes and initiatives.
• To undertake other activities as may be necessary in order to further the execution of the national development agenda, and the objectives mentioned above.
Governing Council of NITI Aayog
• The Governing Council of NITI Aayog, comprising chief ministers of all states and Union Territories with legislatures and Lt Governors of other Union Territories, came into effect on February 16, 2015.
• The Governing Council is chaired by the Prime Minister.
• It also includes Ex-officio members and Special Invitees.
• It is the premier body tasked with evolving a shared vision of national priorities and strategies, with the active involvement of states, in shaping the development narrative.
• The Governing Council, which embodies the objectives of cooperative federalism, presents a platform to discuss inter-sectoral, inter-departmental and federal issues to accelerate the implementation of the national development agenda.
Manorama Yearbook app is now available on Google Play Store and iOS App Store