- World
- Sep 29
What is the significance of CPTPP?
Beijing said it will block Taiwan’s application to join the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), citing as its reason the island’s refusal to concede that it is a part of China.
Taiwan announced on September 23 that it had applied to join the Pacific Rim trade initiative, a week after China submitted its own application.
What is the CPTPP?
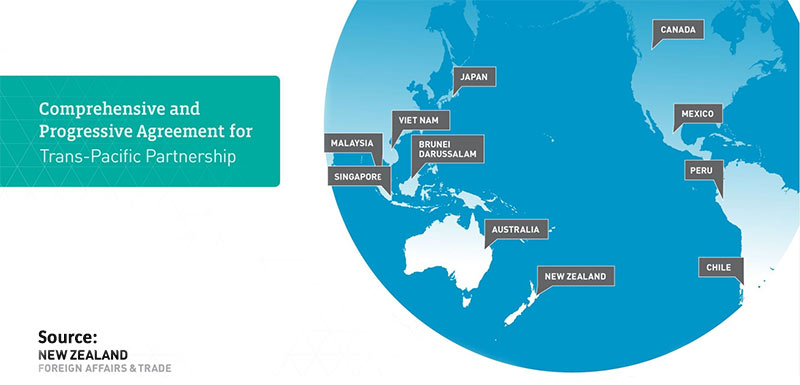
• The Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) is a free trade agreement involving 11 countries around the Pacific Rim.
The countries are:
• New Zealand
• Australia
• Brunei Darussalam
• Canada
• Chile
• Japan
• Malaysia
• Mexico
• Peru
• Singapore
• Vietnam.
When was the CPTPP negotiated?
• Negotiations for what was then simply the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) began in March 2010 and concluded on October 5, 2015.
• The US was party to those talks. But the election of President Donald Trump in 2016 led to its withdrawal from the agreement in 2017 before ratification. The remaining 11 participants scrambled to amend the text of the agreement, and the newly renamed CPTPP was signed in March 2018 in Santiago, Chile. It came into force in December the same year.
• The economies included in the CPTPP account for 13.3 percent of world GDP – worth a total of $10.6 trillion.
• The original TPP (including the US) would have been one of the world’s largest economic blocs.
• The 11 countries have a shared vision of the CPTPP as a platform that is open to others to join if they are able to meet its high standards.
• All 11 countries are members of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC).
• The UK has started negotiating to join after it left the European Union.
• CPTPP goes beyond reducing costs for businesses. It includes commitments to safeguard high labour and environmental standards across the Asia-Pacific region.
• It recognises the challenges facing Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) in establishing export markets, and includes outcomes to help make this task easier in the CPTPP region.
The benefits include:
• Elimination of tariffs and reduction in non-tariff barriers in CPTPP export markets.
• Common and transparent trade and investment rules between 11 Asia-Pacific countries, assisting in the reduction of administration costs.
• Rules that encourage SME participation in government procurement opportunities in all CPTPP countries, including the requirement for suppliers to have access to an independent review body when procurement processes do not comply with the rules.
• Commitments addressing a number of ‘21st century’ trade and investment issues, including rules against corruption, reducing unfair competition by state-owned enterprises, and ensuring a liberalised environment for electronic commerce.
• Longer term integration benefits facilitating better access to regional supply chains for goods and services (also known as Global Value Chains).
Why China opposes Taiwan’s application?
China claims democratically-ruled Taiwan as its own territory, to be brought under its control by force if necessary. It refuses to recognise the island’s government and has increasingly sought to isolate the independence-leaning administration of President Tsai Ing-wen.
China and Taiwan split after the Communist Party seized control of the mainland in 1949 amid a civil war. They have extensive trade and investment ties but no official relations, and China has been using increasingly threatening language toward the island while applying military, diplomatic and economic pressure against it.
Taiwan applied to join the CPTPP using the name Separate Customs Territory of Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen and Matsu. That is the name it used to join the World Trade Organization in 2002.
As it has gained economic and political clout, China has adopted an increasingly rigid attitude toward such organisations in recent years, particularly regarding Taiwan.
Manorama Yearbook app is now available on Google Play Store and iOS App Store