- World
- Apr 09
Explainer - Types of solar eclipses
• Eclipse mania gripped all of Mexico, the US and Canada, as the Moon swept in front of the Sun, blotting out daylight on April 8.
• It was the first total eclipse to sweep across a large swath of North America since 2017, and will be the last one visible from the United States until 2044.
• It took about 80 minutes from the moment the Moon first began to cover the Sun to the moment of totality, then another 80 minutes to complete the process in reverse.
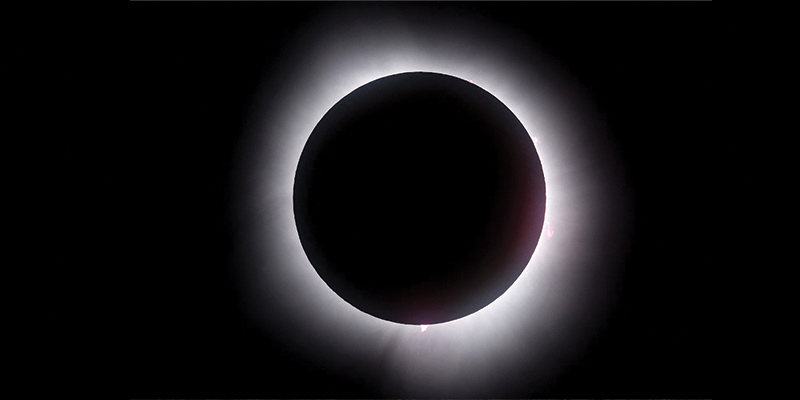
• The last remaining bit of brilliant sunlight before totality creates a “diamond ring effect”, with a single bright spot glaring from one side of the lunar shadow while the Sun’s corona still encircles the rest of the Moon.
• The crowds burst into cheers, applause and whistles when the eclipse reached totality.
• The period of totality lasted up to 4-1/2 minutes depending on the observer’s location.
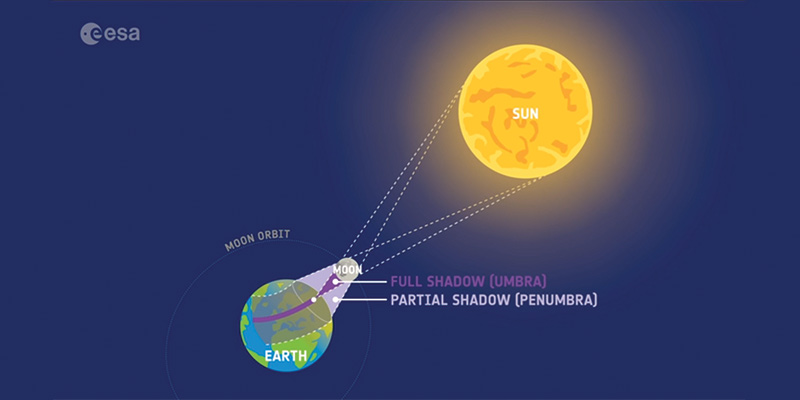
What is a solar eclipse?
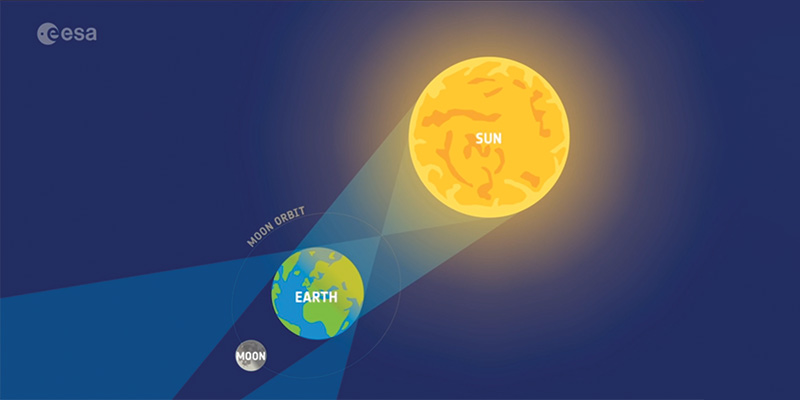
• Two main types of eclipse can be observed from Earth: lunar and solar.
• In a lunar eclipse, Earth is between the Sun and the Moon.
• In a solar eclipse, the Moon is between the Sun and Earth.
• A solar eclipse happens when the Sun, Moon and Earth are perfectly aligned.
• The Moon blocks light from the Sun and casts a shadow on Earth. The eclipse is visible to anybody within this shadow.
Types of solar eclipses:
i) Total Solar Eclipse
During a total solar eclipse, the Sun, Moon and Earth are perfectly aligned and the Moon covers the entire disc of the Sun. A total solar eclipse happens when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, completely blocking the face of the Sun. People located in the center of the Moon’s shadow when it hits Earth will experience a total eclipse. The sky will darken, as if it were dawn or dusk. Weather permitting, people in the path of a total solar eclipse can see the Sun’s corona, the outer atmosphere, which is otherwise usually obscured by the bright face of the Sun.
ii) Annular Solar Eclipse
An annular solar eclipse happens when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, but when it is at or near its farthest point from Earth. Because the Moon is farther away from Earth, it appears smaller than the Sun and does not completely cover the Sun. As a result, the Moon appears as a dark disk on top of a larger, bright disk, creating what looks like a ring around the Moon.
iii) Partial Solar Eclipse
A partial solar eclipse happens when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth but the Sun, Moon, and Earth are not perfectly lined up. Only a part of the Sun will appear to be covered, giving it a crescent shape. During a total or annular solar eclipse, people outside the area covered by the Moon’s inner shadow see a partial solar eclipse.
iv) Hybrid Solar Eclipse
Because Earth’s surface is curved, sometimes an eclipse can shift between annular and total as the Moon’s shadow moves across the globe. This is called a hybrid solar eclipse.
What is a lunar eclipse?
• A lunar eclipse occurs when Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon and (part of) the Moon is shaded by Earth. Lunar eclipses can be seen by anybody on Earth for whom the Moon is above the horizon, and are therefore much more common than solar eclipses. They take place up to five times a year.
• When the Sun, Earth and Moon are well aligned, the Moon is completely covered by Earth’s full central shadow – at these times we see a total lunar eclipse. Some sunlight is refracted onto the Moon through Earth’s atmosphere, giving the Moon a reddish colour.
Manorama Yearbook app is now available on Google Play Store and iOS App Store