- World
- May 23
UK signs deal to hand over Chagos Islands to Mauritius
• The United Kingdom signed an agreement to hand sovereignty over the Chagos Islands to Mauritius on May 22, resolving a long-standing colonial-era dispute.
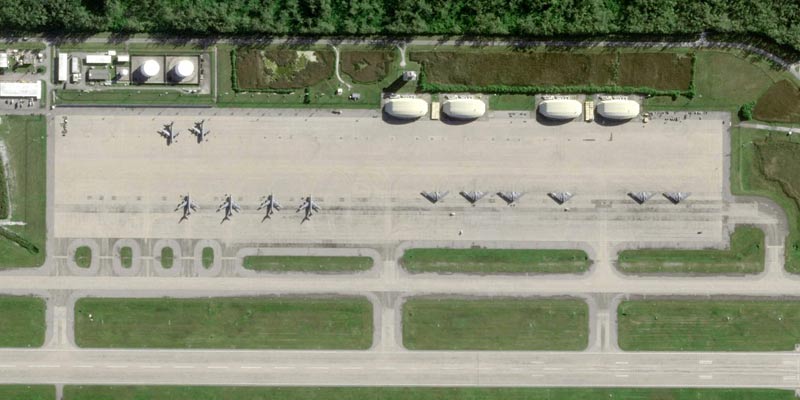
• The Indian Ocean archipelago is home to an important naval and bomber base on the largest of the islands, Diego Garcia, operated by US forces and crucial for British counter-terrorism and intelligence.
• The multibillion-dollar deal will allow Britain to retain control of the strategically important US-UK air base on Diego Garcia, the largest island of the archipelago in the Indian Ocean, under a 99-year lease.
• Under the agreement, the UK will pay Mauritius an average of 101 million pounds ($136 million) a year to lease back the base for at least 99 years.
• The signing ends months of wrangling over the deal, the details of which were first announced in October, after the then-Mauritian leader Pravind Jugnauth was replaced by Prime Minister Navin Ramgoolam, who raised concerns about it.
• It was further delayed after the inauguration of US President Donald Trump in January, with London wanting to give the new administration time to examine the details of the plan.
• In February, Trump indicated his backing for the deal.
• The deal ensures the UK retains full operational control of Diego Garcia, including management of the electromagnetic spectrum satellite used for communications – vital for countering hostile interference.
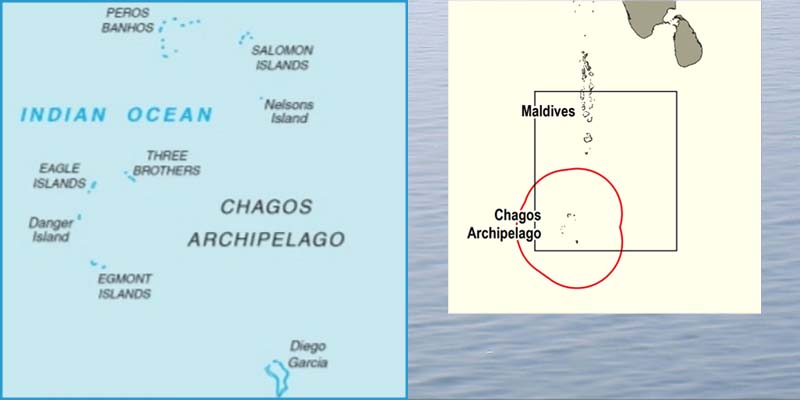
Chagos Islands
• The Chagos Archipelago, located in the Indian Ocean, was separated from Mauritius by the UK in 1965, three years before Mauritius gained independence.
• This move had long been contested, as it involved the forced displacement of around 1,500 Chagossians, who were exiled to Mauritius, Seychelles, and the UK to make way for a US military base on Diego Garcia, the largest of the islands.
• The Chagos archipelago comprises 58 islands, with Diego Garcia being the largest and most significant.
Colonial history of Chagos Islands
• The colonial history of the Chagos Islands began in the 16th century when Portuguese navigators first discovered and mapped the archipelago, naming some of the islands. However, they did not establish any settlements.
• The Dutch were the next to explore the islands, but like the Portuguese, they did not occupy the territory.
• The Chagos Islands later came under French control, alongside Mauritius and Reunion.
• The French, during their colonisation, renamed several islands and established coconut plantations, using enslaved labor from Madagascar and Mozambique.
• Additionally, labourers from southern India were brought to work on the plantations.
• After the defeat of Napoleon in 1814, the French ceded the Chagos Islands, along with Mauritius, to the British under the Treaty of Paris. This marked the beginning of British control, which continued until the recent agreement to return the islands to Mauritius.
Strategic importance of Diego Garcia
• The agreement with Mauritius secures the future of the strategically critical UK-US military base on Diego Garcia.
• The base provides a unique shared platform with irreplaceable security capabilities that enable a UK and US military presence across the Middle East, Indo-Pacific and Africa.
• The base has played a vital role in defending the UK and its allies for over 50 years. This new deal ensures its continued operation for at least the next century, protecting capabilities essential to UK intelligence and counter-terrorism.
• Its deep-water port, airfield, and advanced communications and surveillance capabilities give the UK and its allies crucial strategic capabilities, which have played a key role in missions to disrupt high-value terrorists.
• The base is a critical logistics hub at a strategic location, with a full range of facilities that acts as a key refuelling and resupply station for naval and air operations.
• The base helps protect some of the most important shipping lanes in the world, while also remaining isolated enough to be protected from attack by adversaries.
Base capabilities
Airfield: Location and infrastructure accommodate a broad range of military aircraft, with capability to support military requirements from strike operations to humanitarian response.
Port: A multitude of berthing options for the UK and US navies to support various missions including Carrier Strike Group deployment. The UK maintains a Nuclear Emergency Response Organisation to permit nuclear powered submarines to safely berth at the port. The US uses Diego Garcia to strategically position equipment and supplies at sea for rapid deployment in various global theatres, including for humanitarian aid and disaster relief missions over the years, across the Indo-Pacific.
Seismic monitoring: Permanent location of three pieces of critical Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty monitoring equipment, a network constantly monitoring for indicators of nuclear testing, vital in preventing nuclear proliferation.
Space capabilities: Hosts one of the monitoring stations and one of the four ground antennas for the Global Positioning System (GPS). Also hosts part of the Ground-Base Electro-Optical Deep Space Surveillance (GEODSS) System. This provides situational awareness of objects in Earth’s orbit, helping to track space debris that pose a risk to space systems.
India welcomes the deal
• India has welcomed the UK’s decision to hand over the sovereignty of Chagos Islands to Mauritius.
• India said it has consistently supported Mauritius’s claim over the Chagos Archipelago in keeping with its principled position on “decolonisation, respect for sovereignty, and the territorial integrity of nations”.
• The formal resolution of the longstanding Chagos dispute through this bilateral treaty is a milestone achievement and a positive development for the region, the Ministry of External Affairs said.
• The ministry said the country remains committed to working closely with Mauritius and other like-minded countries to strengthen maritime security and regional stability and ensure peace and prosperity in the Indian Ocean region.
Manorama Yearbook app is now available on Google Play Store and iOS App Store