- World
- Apr 20
NASA’s Ingenuity Mars helicopter succeeds in historic first flight
NASA scored a 21st-century Wright Brothers moment on April 19 as it sent its miniature robot helicopter — Ingenuity — buzzing above the surface of Mars for 39 seconds, marking the first powered controlled flight of an aircraft on another planet.
Officials at the US space agency hailed the brief flight of the 1.8-kg rotorcraft as an achievement that would help pave the way for a new mode of aerial exploration on Mars and other destinations in the solar system.
NASA likened the achievement to the Wright Brothers’ first controlled flight of their motor-driven airplane near Kitty Hawk, North Carolina, in December 1903 — a takeoff and landing that covered just 120 feet (37 meters) in 12 seconds.
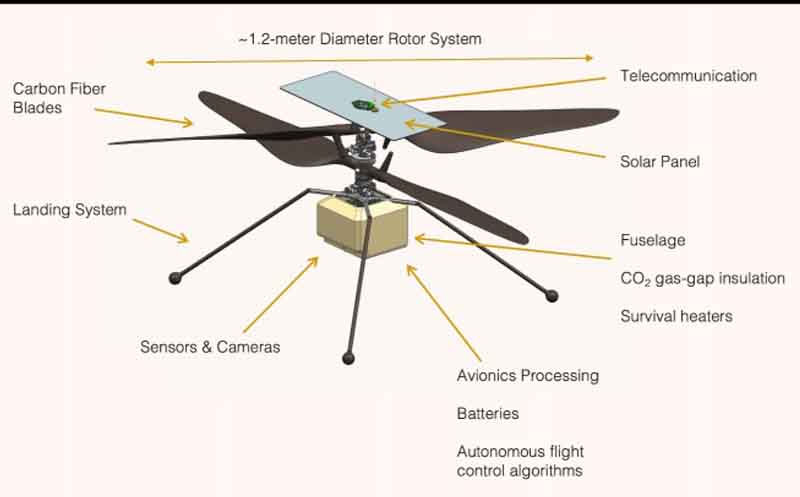
What are the features of Ingenuity?
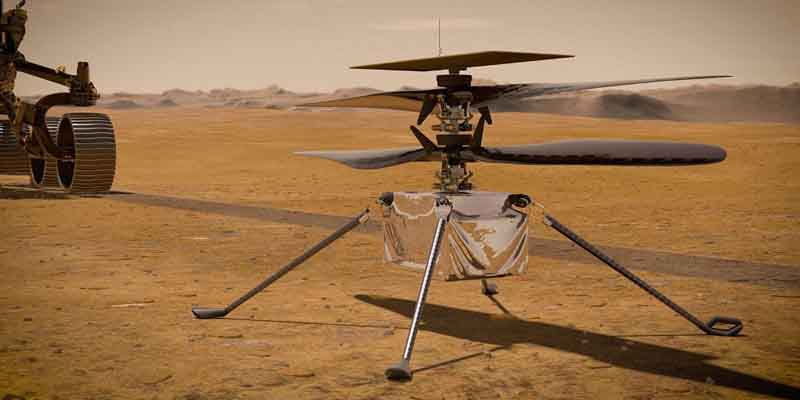
• Ingenuity hitched a ride to Mars on Perseverance, clinging to the rover’s belly upon their arrival in an ancient river delta on February 18.
• More than six years in the making, Ingenuity is a barebones 19 inches (49 cm) tall, a spindly four-legged chopper.
• Its fuselage, containing all the batteries, heaters and sensors, is the size of a tissue box.
• Ingenuity’s rotor system features four carbon-fiber blades arranged into two 4-foot (1.2-meter) counter-rotating rotors that spin at about 2,400 rpm.
• The helicopter is topped with a solar panel for recharging the batteries, crucial for its survival during the (minus)-90 degree-Celsius Martian nights.
How did NASA accomplish this mission?
While Mars possesses much less gravity to overcome than Earth, its atmosphere is just 1 per cent as dense, making it especially difficult to generate aerodynamic lift. To compensate, engineers equipped Ingenuity with rotor blades that are larger (4 feet long) and spin far more rapidly than would be needed on Earth.
The design was successfully tested in vacuum chambers simulating Martian conditions.
Because of the enormous distances involved, Ingenuity was designed to execute pre-programmed flight instructions autonomously, using advanced onboard pilot and navigation systems.
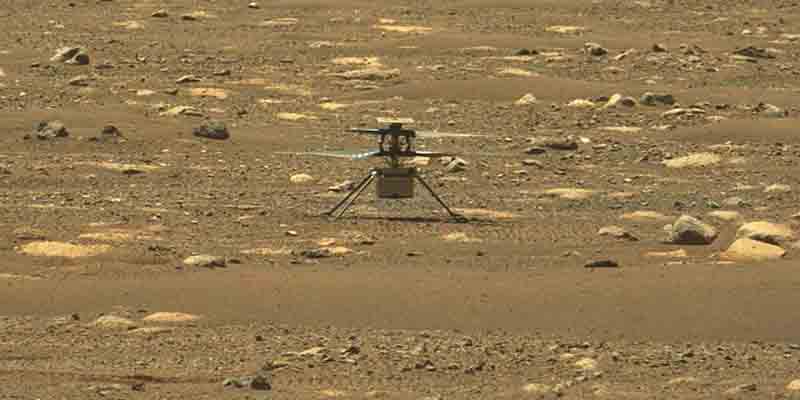
The helicopter was released from the rover to the surface of Jezero Crater on April 3. The first flight was delayed a week by a technical glitch, but NASA resolved the issue by transmitting additional flight sequence commands last week.
NASA chose a flat, relatively rock-free patch for Ingenuity’s airfield, measuring 33 feet by 33 feet (10 meters by 10 meters). It turned out to be less than 100 feet (30 meters) from the original landing site in Jezero Crater.
Flight commands were sent on April 18, after controllers sent up a software correction for the rotor blade spin-up.
Flight controllers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California declared success after receiving the data and images via the Perseverance rover, which stood watch more than 65 meters away.
Early images included a black-and-white still photo taken by a downward-pointing onboard camera while the helicopter was aloft, showing the distinct shadow cast by Ingenuity in the Martian sunlight onto the ground below it. A separate camera mounted on Perseverance captured video of the rotorcraft’s entire flight against the landscape surrounding it.
Despite the flight’s brevity and less-than-soaring altitude, it marked a historic feat in interplanetary aviation, taking place on an “air field” 173 million miles from Earth on the floor of a vast Martian basin called Jezero Crater.
In honour of the modest but monumental first human flight 117 years ago at Kitty Hawk, NASA officially designated Ingenuity’s flight zone as Wright Brothers Field, a location recognised by the International Civil Aviation Organisation in a certificate issued to NASA for the occasion.
Ingenuity is currently on the 16th sol, or Martian day, of its 30-sol (31-Earth days) flight test window. Over the next three sols, the helicopter team will receive and analyse all data and imagery from the test and formulate a plan for the second experimental test flight. If the helicopter survives the second flight test, the Ingenuity team will consider how best to expand the flight profile.
Manorama Yearbook app is now available on Google Play Store and iOS App Store